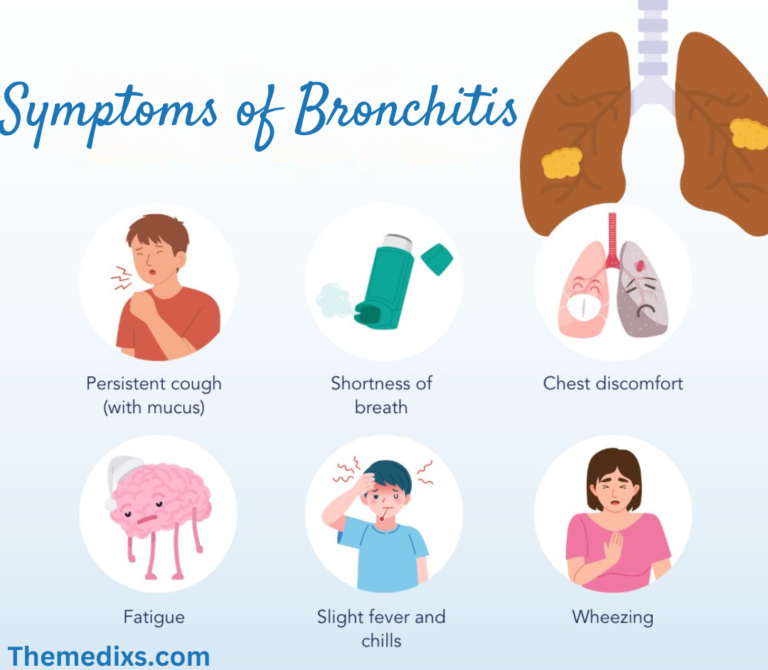
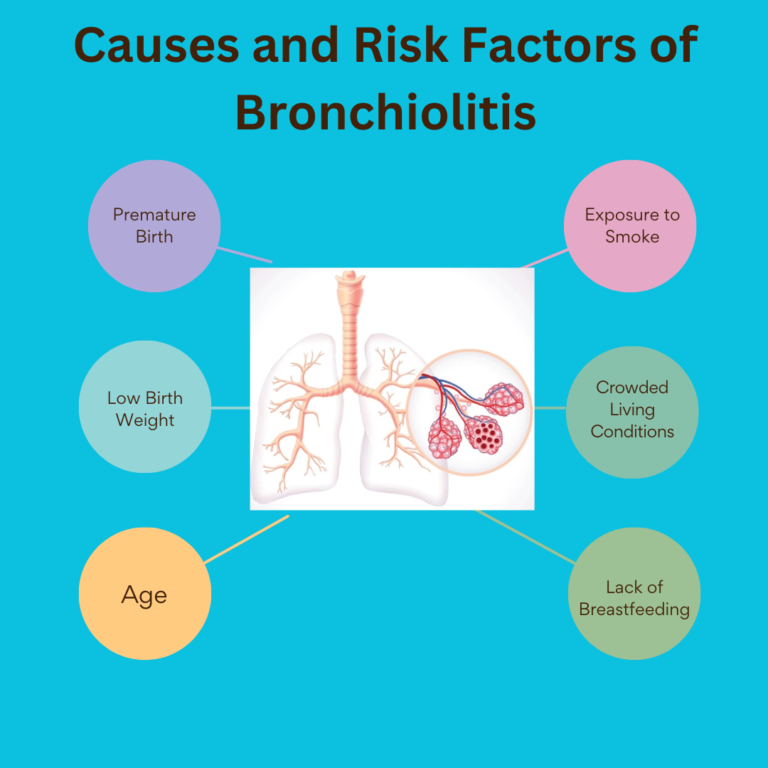
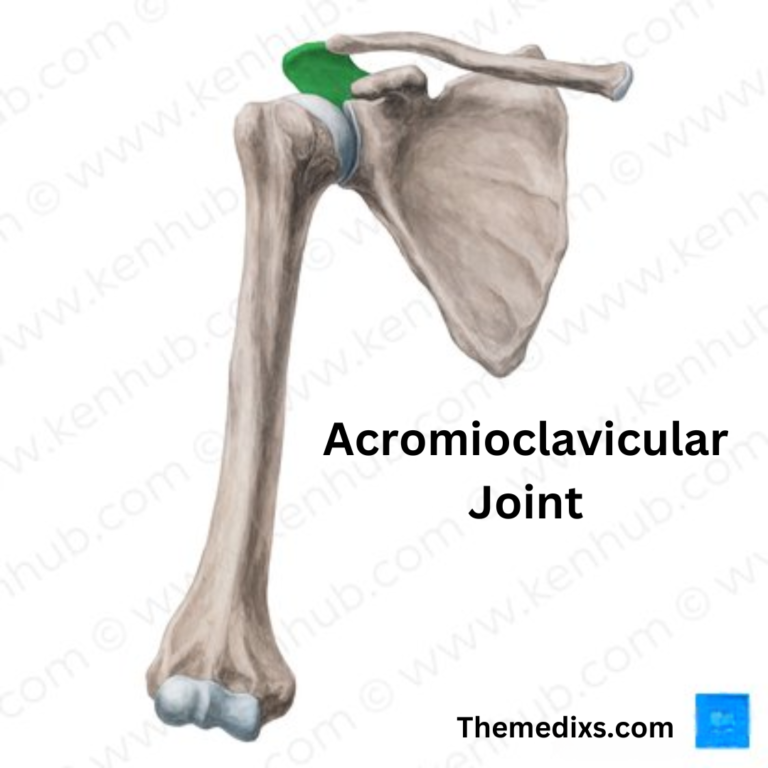
What is Physiotherapy?
Physiotherapy, often referred to as physical therapy, is a vital healthcare profession that focuses on enhancing and restoring functional ability and quality of life to those with physical impairments or disabilities. It employs various techniques to alleviate pain, improve movement, and promote overall health. This blog will explore the essence of physiotherapy, its benefits, techniques, and its crucial role in the recovery process.
Understanding Physiotherapy
At its core, physio-therapy aims to help individuals regain their physical capabilities after injury, surgery, or the onset of illness. Physiotherapists are highly trained professionals who assess, diagnose, and treat physical dysfunctions. They work with patients of all ages and backgrounds, tailoring their approach to meet each individual’s needs.
The History of Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy has ancient roots, tracing back to 460 BC when Hippocrates and later Galen used techniques such as massage and hydrotherapy. The modern practice began in the 20th century, especially during and after World War I, when there was a significant need for rehabilitation services for injured soldiers. Since then, physiotherapy has evolved into a comprehensive field encompassing various treatment methods, technologies, and specialties.
The Role of Physiotherapy in Recovery

1. Pain Management
One of the primary roles of physiotherapy is to manage and alleviate pain. This can be particularly important after an injury or surgery. Physiotherapists employ techniques such as:
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques to manipulate joints and soft tissues.
- Exercise Therapy: Customized exercise programs to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
- Electrotherapy: Use of electrical modalities to reduce pain and promote healing.
By addressing pain directly, physiotherapy helps patients return to their daily activities more quickly and comfortably.
2. Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is a cornerstone of physiotherapy. After surgeries like hip replacements or injuries such as fractures, patients often face limitations in mobility and strength. Physiotherapists develop structured rehabilitation programs that may include:
- Strength Training: Focused exercises to rebuild strength in affected areas.
- Balance and Coordination Exercises: Activities that enhance stability and prevent falls.
- Functional Training: Simulating everyday activities to ensure patients can return to their normal routines.
3. Injury Prevention
An essential aspect of physio-therapy is preventing future injuries. Physiotherapists educate patients about proper body mechanics, posture, and techniques for safe movement. They may also create personalized exercise regimens to enhance strength and flexibility, reducing the risk of injuries in both sports and daily life.
Managing Chronic Conditions
Physiotherapy is beneficial for managing chronic conditions such as arthritis, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Through tailored exercise programs and lifestyle modifications, physiotherapists help patients manage their symptoms effectively. For example:
- Arthritis: Physiotherapy can improve joint mobility and reduce pain through specific exercises and manual therapy.
- Diabetes: Exercise programs can help regulate blood sugar levels and promote overall fitness.
- Cardiovascular Health: Physiotherapists can design cardiovascular rehabilitation programs for patients recovering from heart surgery or heart-related issues.
Techniques Used in Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy encompasses a wide range of techniques and modalities tailored to individual patient needs. Some common approaches include:
1. Manual Therapy
Manual therapy involves hands-on techniques that manipulate muscles and joints. Physiotherapists may use various methods, including joint mobilization and soft tissue massage, to alleviate pain, reduce stiffness, and enhance mobility.
2. Exercise Therapy
Exercise is a fundamental aspect of physiotherapy. Physiotherapists create individualized exercise plans that may include:
- Strength Training: Building muscle strength and endurance.
- Stretching: Enhancing flexibility and reducing tightness.
- Aerobic Conditioning: Improving cardiovascular health through activities like walking, cycling, or swimming.
3. Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy uses electrical modalities to stimulate muscles, reduce pain, and promote healing. Techniques may include:
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): A method to relieve pain through electrical impulses.
- Ultrasound Therapy: Uses sound waves to promote tissue healing and reduce inflammation.
4. Hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy, or water therapy, utilizes the buoyancy and resistance of water to facilitate movement. This technique is particularly effective for patients with joint pain or mobility issues, as the water provides support and reduces strain on the body.
5. Education and Advice
A crucial component of physiotherapy is patient education. Physiotherapists educate patients about their conditions, treatment options, and strategies for managing symptoms. This empowers individuals to take an active role in their recovery, leading to better outcomes.
The Benefits of Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy offers numerous benefits that extend beyond physical recovery. Some key advantages include:
i. Enhanced Mobility and Function
Physiotherapy helps restore movement and function in injured or impaired areas, enabling patients to perform daily activities more easily. Improved mobility leads to increased independence and a better quality of life.
ii. Pain Reduction
Through targeted treatments and exercises, physiotherapy can significantly reduce pain levels, minimizing the need for medication. This is especially beneficial for individuals seeking alternatives to pain management.
iii. Improved Quality of Life
By addressing physical limitations and enhancing mobility, physiotherapy contributes to an overall improved quality of life. Patients often report increased satisfaction and a greater ability to engage in social and recreational activities.
iv. Education and Self-Management
Physiotherapy empowers patients with the knowledge and tools necessary for self-management. Understanding their condition allows individuals to make informed decisions about their health and wellness.
Conclusion
Physiotherapy is an essential pathway to recovery, offering a comprehensive approach to healing and rehabilitation. Whether it’s alleviating pain, restoring function, or preventing future injuries, physiotherapy plays a critical role in promoting health and well-being. With its diverse techniques and personalized treatment plans, physiotherapy not only addresses immediate physical issues but also fosters long-term health benefits. If you or someone you know is struggling with pain or mobility challenges, consider reaching out to a physiotherapist for guidance on your path to recovery.