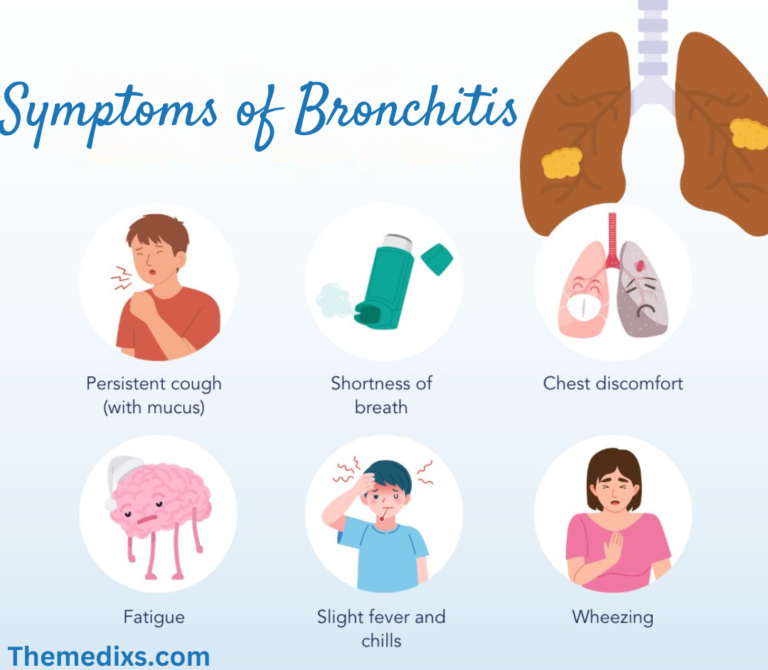
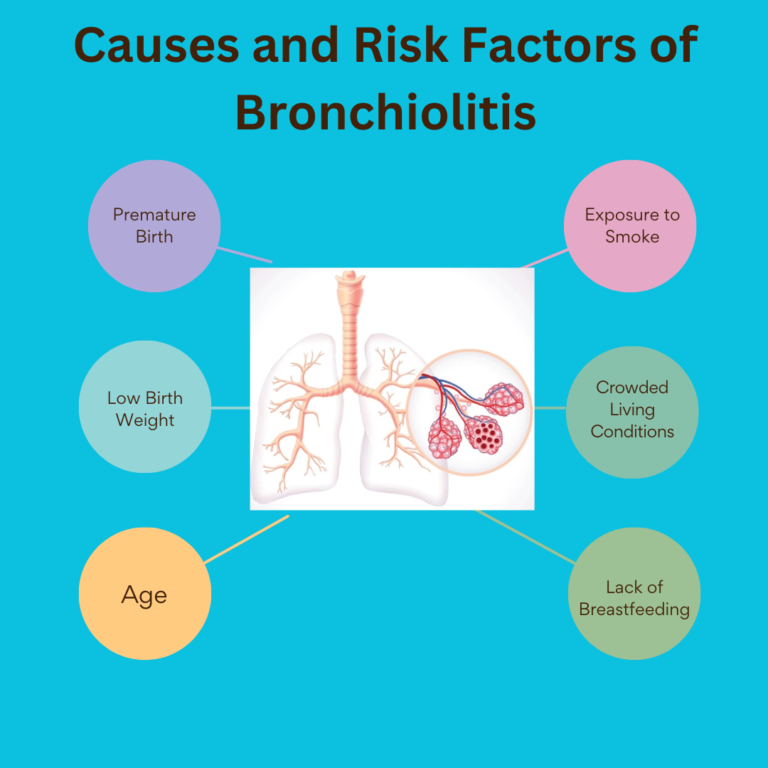
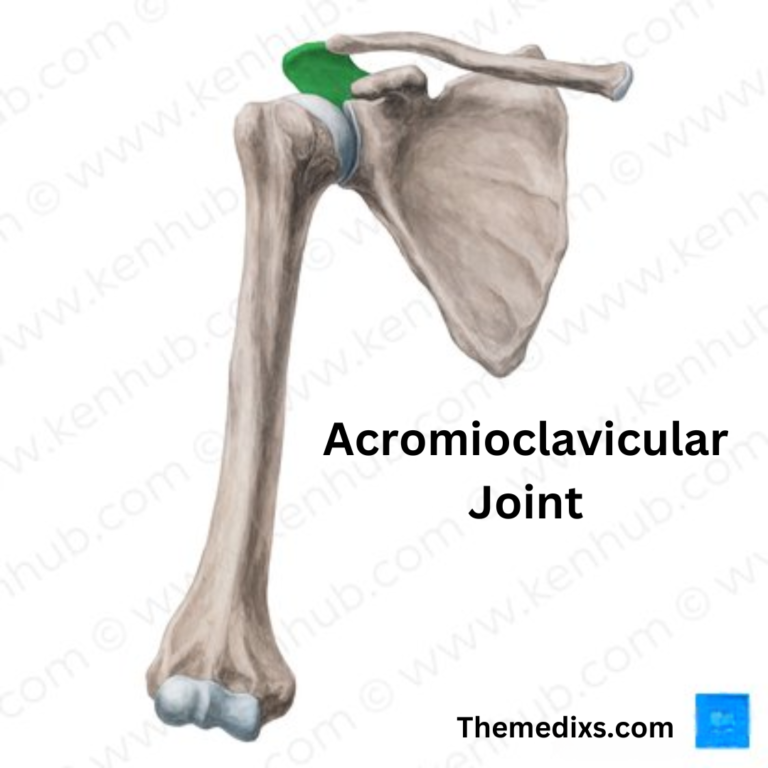
When it comes to rehabilitation and recovery from injuries, the terms “physiotherapy” and “physical therapy” are often used interchangeably. However, despite their similarities, there are important distinctions between the two. This blog will delve into the definitions, methodologies, educational requirements, and cultural differences between physiotherapy and physical therapy, helping you understand which approach may be more suitable for your needs.
Understanding the Terms
What is Physiotherapy?
Physiotherapy is a healthcare profession that focuses on diagnosing, treating, and preventing physical disorders through various physical methods, including exercise, manual therapy, and education. Physiotherapists aim to restore movement and function, improve quality of life, and enhance overall health. The term “physiotherapy” is commonly used in many countries, including the UK, Australia, and Canada.
What is Physical Therapy?
Physical therapy, while essentially serving the same purpose as physiotherapy, is a term primarily used in the United States. Physical therapists (PTs) provide similar services, utilizing exercises, manual techniques, and modalities to help patients recover from injuries, manage pain, and improve mobility. The terminology may vary, but the core principles remain largely the same.
Historical Context
The roots of both physiotherapy and physical therapy can be traced back to the early twentieth century. After World War I, there has been a significant need for rehabilitation services for injured soldiers. Both professions grew in reaction to this demand, evolving into the complete practices we recognize today. However, the 2 phrases have evolved different connotations in numerous regions. In a few countries, “physiotherapy” includes a broader variety of practices and strategies as compared to “bodily remedy” within side the U.S. This difference is vital for understanding how every career is perceived and practiced.
Educational Requirements In Physiotherapy
In countries where physiotherapy is practiced, such as the UK and Canada, physiotherapists typically hold a bachelor’s or master’s degree in physiotherapy from an accredited institution. The educational curriculum includes coursework in anatomy, physiology, biomechanics, and therapeutic techniques. Additionally, students must complete clinical placements to gain hands-on experience.
After graduation, physiotherapists must also pass a licensing examination and register with a regulatory body to practice legally. Continuing education is often required to maintain licensure and stay updated with advancements in the field.
Educational Requirements In Physical Therapy
In the United States, physical therapists usually earn a Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) degree. This three-year program follows an undergraduate degree, encompassing similar coursework to physiotherapy programs, including anatomy, physiology, and therapeutic modalities. Clinical rotations are also a critical component of DPT education, providing real-world experience.
Once they complete their DPT, physical therapists must pass the National Physical Therapy Exam (NPTE) and obtain state licensure to practice. Like physiotherapists, physical therapists engage in ongoing education to keep their skills current.
Treatment Approaches
Physiotherapy Techniques

Physiotherapy is characterized by a holistic approach that considers the entire body and aims to address the root causes of physical issues. Techniques may include:
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques to control joints and soft tissues, relieving pain and improving mobility.
- Exercise Therapy: Customized exercising programs designed to strengthen muscles, enhance flexibility, and enhance normal function.
- Electrotherapy: Use of electrical modalities, including ultrasound or TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation), to control pain and promote healing.
- Hydrotherapy: Utilization of water for therapeutic purposes, frequently effective for joint and muscle rehabilitation.
- Education and Self-Management: Teaching patients about their conditions and techniques to manage signs and symptoms independently.
Physical Therapy Techniques

While many techniques overlap with physiotherapy, physical therapy may place a stronger emphasis on rehabilitation from specific injuries or surgical interventions. Common methods include:
- Therapeutic Exercises: Focused programs aimed toward restoring strength, flexibility, and function.
- Manual Therapy: Similar to physiotherapy, PTs make use of hands-on strategies to improve mobility and decrease pain.
- Modalities: Physical therapists often use modalities including heat, cold, electric stimulation, and ultrasound to aid in recovery.
- Functional Training: Helping patients regain the ability to perform daily activities via targeted exercises.
- Posture and Body Mechanics Training: Educating patients on proper strategies to prevent accidents during everyday tasks
Scope of Practice

Scope of Practice In Physiotherapy
Physiotherapists often have a broader scope of practice, which may include:
- Assessment and Diagnosis: Physiotherapists are educated to assess and diagnose numerous physical conditions, allowing for targeted treatment plans.
- Preventative Care: Many physiotherapists focus on preventing injuries and dealing with chronic situations via exercising and education.
- Chronic Pain Management: Physiotherapists may specialize in treating long-term pain situations, the usage of a combination of strategies to enhance quality of life.
Scope of Practice In Physical Therapy
Physical therapists generally focus on rehabilitation following specific injuries or surgeries. Their scope of practice may include:
- Rehabilitation: Assisting patients in recovering from surgeries, sports injuries, or injuries via tailored programs.
- Return-to-Sport Programs: Physical therapists frequently work with athletes to make sure safe and effective return to their sport following injury.
- Short-Term Rehabilitation: Physical therapy can be extra focused on short-term rehabilitation goals, emphasizing healing over prevention.
Cultural Differences
Global Perspectives
The terminology and practice of physiotherapy versus physical therapy can vary significantly throughout different countries. In many countries, physiotherapy is a well-established profession with a vast scope that consists of not only rehabilitation but also fitness promotion and preventive care.
United States
In the U.S., physical therapy is frequently seen as a specialized field primarily focused on rehabilitation. Insurance coverage and healthcare guidelines can effect how services are delivered, with many patients requiring a referral from a physician to access physical therapy.
Other Countries
In countries like the UK and Australia, physiotherapy is integrated into the healthcare system more holistically. Physiotherapists may work in various settings, including hospitals, clinics, and community health centers, often taking a more proactive role in public health and preventive care.
Which Is Right for You?
When deciding between physiotherapy and physical therapy, consider the following:
- Nature of the Condition: If you require rehabilitation after surgery or a specific injury, either option can be effective. However, if you’re looking for preventive care or holistic management of chronic pain, physiotherapy may be more appropriate.
- Location and Accessibility: Depending on where you live, one term may be more commonly recognized than the other. Ensure that you seek professionals who are licensed and qualified, regardless of the terminology used.
- Personal Preference: The approach and techniques used may vary between physiotherapists and physical therapists. It can be helpful to consult with both to determine which aligns better with your goals and comfort level.
Conclusion
While physiotherapy and physical therapy serve similar purposes in helping individuals recover from physical ailments, understanding their distinctions is crucial for making informed healthcare choices. Both fields offer unique approaches to rehabilitation, with varying educational requirements, treatment techniques, and scopes of practice.
Whether you choose physiotherapy or physical therapy, working with qualified professionals can lead to improved mobility, pain management, and overall health. As you embark on your recovery journey, consider your specific needs and preferences to find the best fit for you. Remember, the ultimate goal is to regain function, enhance quality of life, and promote long-term well-being.